

Gram positive cocci in clusters skin#
Staphylococcus epidermidis are normal flora of the human skin and mucous membranes. Read more about Staphylococcus saprophyticus characteristics and diagnosis. coli as a cause of community-acquired UTIs. Staphylococcus saprophyticus is found primarily on the mucosa of the genital tract in young women and causes urinary tract infections (UTI), especially cystitis in sexually active young women. Bactericidal agent vancomycin is used for the effective treatment of MRSA infections. aureus, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), are highly resistant to multiple antibiotics. Find more about the Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors. aureus are coagulase, collagenase, hyaluronidase, immunoglobulin proteases, protein A, toxic shock syndrome toxin (TSST-1), enterotoxin, exfoliatin, etc. aureus are sepsis, pneumonia, wound infections, folliculitis, necrotizing fasciitis, scalded skin syndrome, surgical site infection, toxic shock syndrome, and food poisoning. It is catalase and coagulase positive gram-positive cocci. Staphylooccus aureus is a normal flora of the nose and skin but also one of the notorious pathogens.
Gram positive cocci in clusters free#
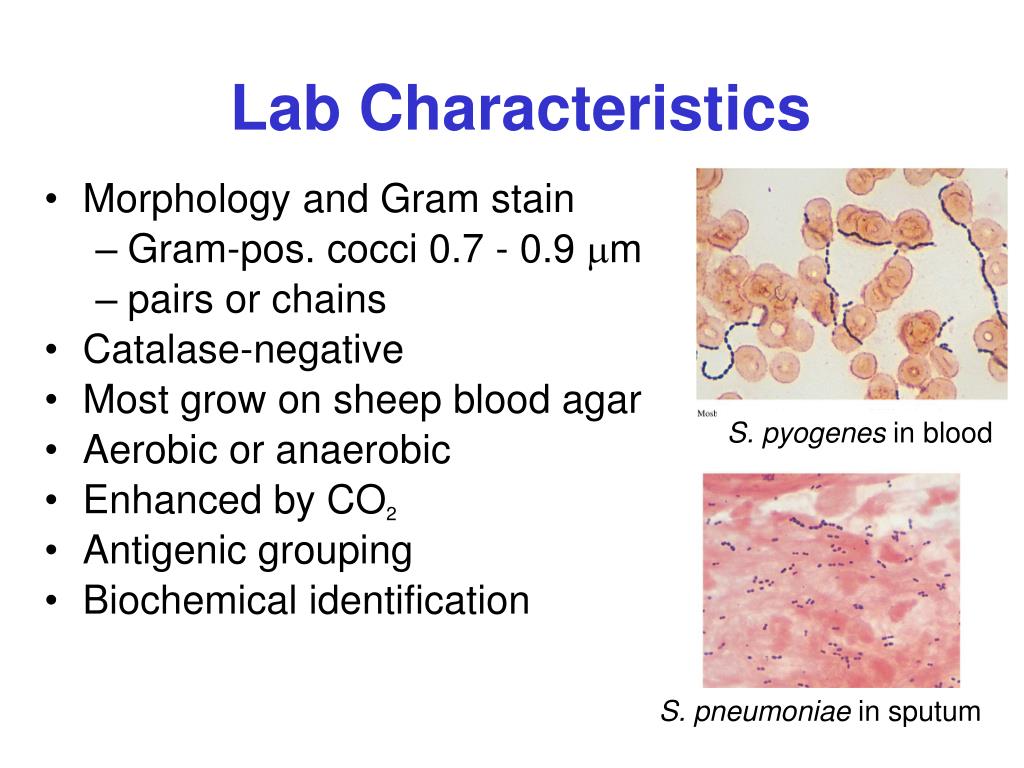
Staphylococcus aureus beta-hemolysis Staphylococcus aureus yellow pigment Staphylococcus aureus without yellow pigment (staphyloxanthin) Clumping factor (cell-bound coagulase) and free coagulase Natrium chloride tolerance (7.5-10%) and mannitol fermentation Lecithinase production and lipase activity on Baird Parker agar Hyaluronidase production (decapsulation test with S.equi ssp.Staphylococcus in Gram Stain Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus colonies on agar cultivation media Staphylococcus aureus on blood agar EUCAST (detection of resistance mechanisms).Selection of appropriate antibiotics depends on diagnosis!! hyaluronidase production (positive decapsulation test with S.equi)Īntibiotic treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections.presence of clumping factor (cell-bound coagulase).production of coagulase (free coagulase).Staphylococcus aureus basic characteristics (infection of the heart valves) and pneumonia, which may be rapidly spread.Ībbreviated from Wikipedia. Prosthetic joints put a person at particular risk for septic arthritis, and staphylococcal endocarditis aureus infection canĬause a severe disease Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS).ĭeeply penetrating S. This leads to furuncles (boils) and carbuncles (a collection of furuncles). aureus can infect other tissues when barriers have been breached (e.g., skin or mucosal lining). It can survive on domesticated animals such as dogs, cats and horses. aureus under these circumstancesĭoes not always indicate infection and therefore does not always require treatment (indeed, treatment may be ineffective and re-colonisation may occur). ( in about a third of the population) and throat less commonly. Staphylococcus aureus may occur as a commensal on human skin it also occurs in the nose frequently Of certain color, depending on used pH indicator (in this picture pink). MRSA is able to grow on this media and produce colonies MRSA) often have only weak or no beta-hemolysis and special cultivation media with oxacillin, mannitol and NaCl for their isolation are used. Methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus (i.e. The golden appearance of colonies of some strains is the etymological root of the bacteria's name aureus meaning " golden" in Latin. On blood agar plates, colonies of Staphylococcus aureusĪre frequently surrounded by zones of clear beta-hemolysis.

Individual colonies on agar are round, convex, and 1-4 mm in diameter with a sharp border. Staphylococcus aureus on Columbia agar with 5% defibrinated sheep blood (Bio-Rad™).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
